Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
CVPR
2009
IEEE
2009
IEEE
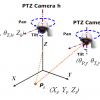
Cooperative Mapping of Multiple PTZ Cameras in Automated Surveillance Systems
Due to the capacity of pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) cameras to
simultaneously cover a panoramic area and maintain high
resolution imagery, researches in automated surveillance
systems with multiple PTZ cameras have become
increasingly important. Most existing algorithms require
the prior knowledge of intrinsic parameters of the PTZ
camera to infer the relative positioning and orientation
among multiple PTZ cameras. To overcome this
limitation, we propose a novel mapping algorithm that
derives the relative positioning and orientation between
two PTZ cameras based on a unified polynomial model.
This reduces the dependence on the knowledge of intrinsic
parameters of PTZ camera and relative positions.
Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed
algorithm presents substantially reduced computational
complexity and improved flexibility at the cost of slightly
decreased pixel accuracy, as compared with the work of
Chen and Wang. This slightly decreased pixel accuracy
can be co...
| Added | 09 May 2009 |
| Updated | 10 Dec 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2009 |
| Where | CVPR |
| Authors | Andreas Koschan, Anis Drira, Chung-Chen Chen, Mongi A. Abidi, Yi Yao |
Comments (0)