Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
ISBI
2008
IEEE
2008
IEEE
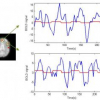
FMRI brain activity and underlying hemodynamics estimation in a new Bayesian framework
The emerging functional MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), fMRI, imaging modality was developed to obtain non-invasive information regarding the neural processes behind pre-determined task. The data is gathered in such a way that the extraction certainty of the desired information is maximized. Still this is a difficult task due to low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), corrupting noise and artifacts from several sources. The most prevalent method, here called SPM-GLM [1] uses a conventional statistical inference methodology based on the t-statistics, where it assumes a rather rigid shape on the BOLD Hemodynamic Response Function (HRF), constant for the whole region of interest (ROI). A new algorithm, designed in a Bayesian framework, is presented in this paper, called SPM-MAP. The algorithm jointly detects the brain activated regions and the underlying HRF in an adaptative and local basis. This approach presents two main advantages: 1) the activity detection benefits from the method's ...
Related Content
| Added | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Updated | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2008 |
| Where | ISBI |
| Authors | David M. Afonso, João M. Sanches, Martin H. Lauterbach |
Comments (0)