Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
ISBI
2006
IEEE
2006
IEEE
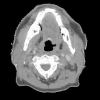
Head and neck lymph node region delineation using a hybrid image registration method
The success of radiation therapy depends critically on accurately delineating the target volume, which is the region of known or suspected disease in a patient. Methods that can compute a contour set defining a target volume on a set of patient's biomedical images will contribute greatly to the success of radiation therapy and drastically reduce the workload of radiation oncologists, who currently often draw the targets by hand on images using simple computer drawing tools. We are developing methods for automatically selecting and adapting standardized regions of tumor spread based on the location of lymph node regions in a standard or reference case, using image registration techniques. Previously available image registration techniques (deformable transformations computed using mutual information [5]) appear promising and can be supplemented by utilizing landmark correspondences in the optimization process to come closer to achieving a clinically acceptable match.
Image Registration Techniques | ISBI 2006 | Lymph Node Regions | Medical Imaging | Radiation Therapy |
| Added | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Updated | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2006 |
| Where | ISBI |
| Authors | Chia-Chi Teng, Linda G. Shapiro, Ira Kalet |
Comments (0)