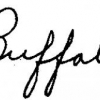Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
107
click to vote
CVPR
1998
IEEE
1998
IEEE
A Methodology for Deriving Probabilistic Correctness Measures from Recognizers
This paper describes the derivation of probability of correctness from scores assigned by most recognizers. Motivation for this research is three-fold: i probability values can be used to rerank the output of any recognizer by using a new set of training data; if the training data is su ciently large and representative of the test data, the recognition rates are seen to improve signi cantly, ii derivation of probability values puts the output of di erent recognizers on the same scale; this makes comparison across recognizers trivial, and iii word recognition can be readily extended to phrase and sentence recognition because the integration of language models becomes straightforward. We have conducted an extensive set of experiments. The results show a reranking of recognition choices based on the derived probability values leading to an enhancement in performance.
Computer Vision | CVPR 1998 | Di Erent Recognizers | Probability Values | Recognition Choices | Recognition Rates | Word Recognition |
Related Content
| Added | 12 Oct 2009 |
| Updated | 30 Oct 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 1998 |
| Where | CVPR |
| Authors | Djamel Bouchaffra, Venu Govindaraju, Sargur N. Srihari |
Comments (0)