ICC
2009
IEEE
14 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
—In a wireless sensor network, an adversary equipped monitoring antenna can easily overhear packets, which may facilitate identifying the directions of packet flows and trace to ...
CCS
2009
ACM
14 years 6 months ago
2009
ACM
In mobile networks, authentication is a required primitive of the majority of security protocols. However, an adversary can track the location of mobile nodes by monitoring pseudo...
MSWIM
2009
ACM
14 years 6 months ago
2009
ACM
Wireless sensor networks have attracted increasing attentions considering their potentials for being widely adopted in both emerging civil and military applications. A common prac...
MOBISYS
2007
ACM
14 years 11 months ago
2007
ACM
The broadcast and tetherless nature of wireless networks and the widespread deployment of Wi-Fi hotspots makes it easy to remotely locate a user by observing her wireless signals....
102
click to vote
GIS
2009
ACM
15 years 18 days ago
2009
ACM
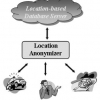
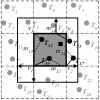
The k-anonymity technique is widely used to provide location privacy protection for accessing location-based services (LBS), i.e., the exact location of a query initiator is cloak...
Publication
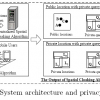
The wide spread of location-based services results in a strong market for location-detection devices (e.g., GPS-like devices, RFIDs, handheld devices, and cellular phones). Example...
Publication
This paper tackles a major privacy threat in current location-based services where users have to report their exact locations to the database server in order to obtain their desire...
VLDB
2006
ACM
15 years 11 months ago
2006
ACM
This paper tackles a major privacy concern in current location-based services where users have to continuously report their locations to the database server in order to obtain the ...
Publication
Existing location-based services provide specialized services to their customers based on the knowledge of their exact locations. With untrustworthy servers, location-based service...
159
click to vote
Tutorial
The explosive growth of location-detection devices (e.g., GPS-like devices and handheld devices) along with wireless communications and mobile databases results in realizing locati...