Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
ICIP
2000
IEEE
2000
IEEE
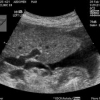
Joint Space-Frequency Segmentation, Entropy Coding and the Compression of Ultrasound Images
Joint space-frequency segmentation is a relatively new image compression technique that finds the rate-distortion optimal representation of an image from a large set of possible spacefrequency partitions and quantizer combinations. As such, the method is especially effective when the images to code are statistically inhomogeneous, which is certainly the case in the ultrasound modality. Unfortunately, however, the original paper on space-frequency segmentation neglected to use an actual entropy coder, but instead relied upon the zeroth-order entropy to guide the algorithm. In this work, we fill the above gap by comparing actual entropy-coding strategies and their effect on both the resulting segmentations as well as the rate-distortion performance. We then apply the resulting "complete" algorithm to representative ultrasound images. The result is an effective technique that performs significantly better than SPIHT using both objective and subjective measures.
Actual Entropy Coder | ICIP 2000 | Image Compression Technique | Image Processing | Rate-distortion Optimal Representation |
| Added | 25 Oct 2009 |
| Updated | 27 Oct 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2000 |
| Where | ICIP |
| Authors | Ed Chiu, Jacques Vaisey, M. Stella Atkins |
Comments (0)