Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
ICPR
2006
IEEE
2006
IEEE
Isomap Based on the Image Euclidean Distance
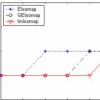
Scientists find that the human perception is based on the similarity on the manifold of data set. Isometric feature mapping (Isomap) is one of the representative techniques of manifold. It is intuitive, well understood and produces reasonable mapping results. However, if the input data for manifold learning are corrupted with noises, the Isomap algorithm is topologically unstable. In this paper, we present an improved manifold learning method when the input data are images--the Image Euclidean distance based Isomap (ImIsomap), in which we use a new distance for images called IMage Euclidean Distance (IMED). Experimental results demonstrate a consistent performance improvement of the algorithm ImIsomap over the traditional Isomap based on Euclidean distance.
Computer Vision | Distance Based Isomap | ICPR 2006 | Image Euclidean Distance | Manifold Learning Method |
Related Content
| Added | 09 Nov 2009 |
| Updated | 09 Nov 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2006 |
| Where | ICPR |
| Authors | Jie Chen, Ruiping Wang, Shiguang Shan, Wen Gao, Xilin Chen |
Comments (0)