Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
103
click to vote
ISBI
2008
IEEE
2008
IEEE
Invariant 3D spharm features for characterizing fMRI activations in ROIs while minimizing effects of intersubject anatomical var
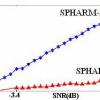
Spatial patterns of activation statistics within anatomically-defined regions of interest (ROIs) in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data were recently shown to be sensitive markers of brain activation changes. Most current methods that analyze fMRI activation statistics largely ignore this. The accuracy and validity of the prevalent approach of spatial normalization of functional data is also being debated. In this paper we present a novel spherical harmonics based rotational, translation and scale invariant feature representation of fMRI data which allows for direct quantification of activation patterns within ROIs without any need for spatial normalization. We also present a novel parallel technique for quantifying anatomical properties of the ROIs where we employ a principal component based approach to reduce the effects of anatomical variability in the ROI on functional pattern analysis. We validate our proposed method and demonstrate its improved sensitivity over con...
Brain Activation Changes | FMRI Activation Statistics | ISBI 2008 | Medical Imaging | Simulated FMRI Data |
| Added | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Updated | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2008 |
| Where | ISBI |
| Authors | Ashish Uthama, Rafeef Abugharbieh, Samantha J. Palmer, Anthony Traboulsee, Martin J. McKeown |
Comments (0)