Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
103
click to vote
ISBI
2008
IEEE
2008
IEEE
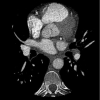
Analysis and mitigation of calcium artifacts in cardiac multidetector CT
Multi-detector Computed Tomography offers the promise of a non-invasive alternative to invasive coronary angiography for the evaluation of coronary artery disease. An impediment preventing its widespread adoption is the presence of image "blooming" artifacts due to the presence vascular calcium. This blooming has been linked to cardiac motion, beam hardening, and resolution effects. In this paper we study the contribution of these elements to blooming in a controlled way and conclude that the strongest effect for current systems is due to resolution. We then present a multicomponent algebraic-type reconstruction approach to mitigate such blooming artifacts, motivated by recent results in image inpainting. The reconstruction approach decomposes the image into a collection of spatially localized components, each with a set of homogeneous properties. The local nature of the decomposition and constraints prevents artifacts from contaminating other image regions.
Constraints Prevents Artifacts | Coronary Artery Disease | Invasive Coronary Angiography | ISBI 2008 | Medical Imaging |
| Added | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Updated | 20 Nov 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2008 |
| Where | ISBI |
| Authors | Zhuangli Liang, W. Clem Karl, Synho Do, Thomas Brady, Homer H. Pien |
Comments (0)