Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
ICIP
2008
IEEE
2008
IEEE
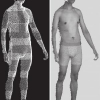
A robot-based 3D body scanning system using passive stereo vision
This paper proposes a three-dimensional (3D) body scanning system that uses passive stereo vision with a robot arm. So far, the reported 3D body scanning systems employ active 3D measurement methods. However, active methods use structured illumination or laser scanning, which is not desirable in many systems applied to human. A major problem of using passive stereo vision for 3D measurement is its low accuracy. In addition, multiple stereo images captured from different viewpoints are necessary to cover the whole body at an appropriate distance. Addressing these problems, we have newly developed an eye-in-hand system based on passive stereo vision, where a phase-based image matching technique is employed for sub-pixel disparity estimation. Through a set of experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed system can capture 3D shape of human body with high quality.
Active 3D Measurement | Body Scanning Systems | ICIP 2008 | Image Processing | Multiple Stereo Images | Passive Stereo Vision | Sub-pixel Disparity Estimation |
| Added | 20 Oct 2009 |
| Updated | 27 Oct 2009 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2008 |
| Where | ICIP |
| Authors | Kazuyuki Miyazawa, Takafumi Aoki |
Comments (0)