Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
142
Voted
VISUALIZATION
2005
IEEE
2005
IEEE
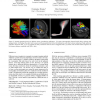
Visualization of White Matter Tracts with Wrapped Streamlines
Diffusion tensor imaging is a magnetic resonance imaging method which has gained increasing importance in neuroscience and especially in neurosurgery. It acquires diffusion properties represented by a symmetric 2nd order tensor for each voxel in the gathered dataset. From the medical point of view, the data is of special interest due to different diffusion characteristics of varying brain tissue allowing conclusions about the underlying structures such as white matter tracts. An obvious way to visualize this data is to focus on the anisotropic areas using the major eigenvector for tractography and rendering lines for visualization of the simulation results. Our approach extends this technique to avoid line representation since lines lead to very complex illustrations and furthermore are mistakable. Instead, we generate surfaces wrapping bundles of lines. Thereby, a more intuitive representation of different tracts is achieved. CR Categories: I.3.8 [Computer Graphics]: Applications J.3...
Diffusion Properties | Diffusion Tensor Imaging | Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Visualization | VISUALIZATION 2005 |
Related Content
| Added | 25 Jun 2010 |
| Updated | 25 Jun 2010 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2005 |
| Where | VISUALIZATION |
| Authors | Frank Enders, Natascha Sauber, Dorit Merhof, Peter Hastreiter, Christopher Nimsky, Marc Stamminger |
Comments (0)