Free Online Productivity Tools
i2Speak
i2Symbol
i2OCR
iTex2Img
iWeb2Print
iWeb2Shot
i2Type
iPdf2Split
iPdf2Merge
i2Bopomofo
i2Arabic
i2Style
i2Image
i2PDF
iLatex2Rtf
Sci2ools
159
click to vote
CVPR
2009
IEEE
2009
IEEE
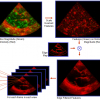
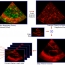
Echocardiogram View Classification using Edge Filtered Scale-invariant Motion Features
In an 2D echocardiogram exam, an ultrasound probe
samples the heart with 2D slices. Changing the orientation
and position on the probe changes the slice viewpoint, altering
the cardiac anatomy being imaged. The determination
of the probe viewpoint forms an essential step in automatic
cardiac echo image analysis. In this paper we present a
system for automatic view classification that exploits cues
from both cardiac structure and motion in echocardiogram
videos. In our framework, each image from the echocardiogram
video is represented by a set of novel salient features.
We locate these features at scale invariant points in
the edge-filtered motion magnitude images and encode them
using local spatial, textural and kinetic information. Training
in our system involves learning a hierarchical feature
dictionary and parameters of a Pyramid Matching Kernel
based Support Vector Machine. While testing, each image,
classified independently, casts a votes towards parent video
cla...
| Added | 09 May 2009 |
| Updated | 04 Jul 2010 |
| Type | Conference |
| Year | 2009 |
| Where | CVPR |
| Authors | Ritwik Kumar, Fei Wang, David Beymer, Tanveer Fathima Syeda-Mahmood |
Comments (0)