106
click to vote
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
A key ingredient in the design of visual object classification
systems is the identification of relevant class specific
aspects while being robust to intra-class variations. Whil...
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
We present methods for training high quality object detectors
very quickly. The core contribution is a pair of fast
training algorithms for piece-wise linear classifiers, which
...
109
click to vote
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
Object tracking typically relies on a dynamic model to
predict the object’s location from its past trajectory. In
crowded scenarios a strong dynamic model is particularly
impo...
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
We describe a method for producing a smooth, stabilized
video from the shaky input of a hand-held light field video camera—
specifically, a small camera array. Traditional stab...
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
We propose a novel approach to reconstruct complete
3D deformable models over time by a single depth camera,
provided that most parts of the models are observed by the
camera at...
101
click to vote
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
This purely theoretical work investigates the problem
of artificial singularities in camera self-calibration. Selfcalibration
allows one to upgrade a projective reconstruction
t...
108
Voted
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
The classical approach to depth from defocus uses two
images taken with circular apertures of different sizes. We
show in this paper that the use of a circular aperture
severely...
110
click to vote
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
High-level, or holistic, scene understanding involves
reasoning about objects, regions, and the 3D relationships
between them. This requires a representation above the
level of ...
88
Voted
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
User-provided object bounding box is a simple and
popular interaction paradigm considered by many existing
interactive image segmentation frameworks. However,
these frameworks t...
114
Voted
ICCV
2009
IEEE
16 years 6 months ago
2009
IEEE
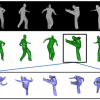
In this paper, we investigate the detection of semantic
human actions in complex scenes. Unlike conventional
action recognition in well-controlled environments,
action detection...